Rediscovering the Architects of Sexology
May 23, 2024
Sigmund Freud and His Impact on Sexology
June 28, 2024Table of Contents
Introduction
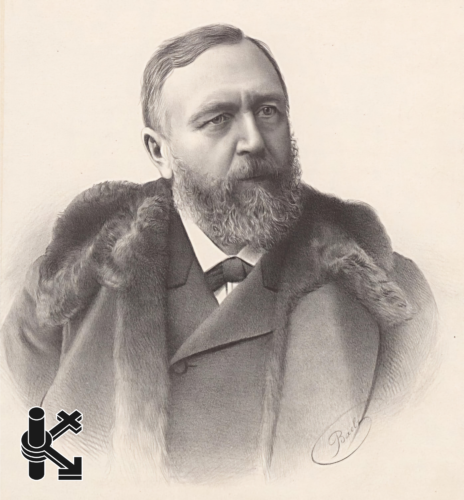
Unveiling the Legacy of Richard von Krafft-Ebing
Richard von Krafft-Ebing (1840–1902) was a monumental figure in the history of sexology. As one of the first psychiatrists to study human sexuality scientifically, he helped lay the foundation for what we now understand as vintage sexology. His landmark work, Psychopathia Sexualis, not only categorized various sexual behaviors but also paved the way for modern sex therapy and discussions on sexual diversity.
This article delves into Krafft-Ebing’s life, his seminal contributions, and the enduring impact of his work on sexology and mental health. His influence continues to shape our understanding of human sexuality today.
Early Life and Personal Background
Richard von Krafft-Ebing was born on August 14, 1840, in Mannheim, Germany. He grew up in a well-educated family that valued academic achievement. From a young age, Krafft-Ebing displayed a deep interest in understanding human behavior. He spent much of his time reading books on philosophy and medicine.
Krafft-Ebing’s personal life was marked by intellectual curiosity and a commitment to his work. Although he had a clinical demeanor, he was known among friends and colleagues for his dry sense of humor and compassion for his patients. His interest in human sexuality may have been influenced by his observations of societal stigmas and the struggles of misunderstood individuals.
Marriage and Family Life
Krafft-Ebing valued family life alongside his dedication to his career. In 1874, he married Maria Luise von Ploennies. Their union was supportive and intellectually stimulating. Maria, a writer and translator, played a crucial role in helping Krafft-Ebing refine his works. She also helped him engage with cultural and literary circles.
Their relationship provided Krafft-Ebing with emotional support and allowed him to pursue his intellectual interests. The balance between family and work was important to him throughout his life.

Richard Freiherr von Krafft-Ebing with his wife Marie Luise
Challenges in His Era
Living in the conservative social climate of the late 19th century, Krafft-Ebing faced criticism for his progressive views on sexuality. Despite societal pressures, he remained committed to the scientific exploration of sexual behavior. He believed that understanding human desires was key to addressing mental health issues.
Therefore, Krafft-Ebing continued his research, even in the face of opposition from traditionalists. His persistence contributed greatly to the advancement of the scientific study of human sexuality.
Contributions to Vintage Sexology and Modern Practices
Krafft-Ebing’s legacy extends far beyond the pages of his book. His efforts laid the groundwork for the evolution of sex therapy and the scientific study of human sexuality, which continue to influence modern practices today.
Recognition of Sexual Diversity
Krafft-Ebing’s research challenged the rigid norms of his time, advocating for a more nuanced understanding of sexual behaviors. Although he often used terms that modern readers might find stigmatizing, his recognition of sexual diversity marked a crucial step toward normalizing discussions around non-heteronormative identities. As a result, his work helped to broaden the conversation on sexuality and contributed to a shift in societal attitudes toward different sexual identities.
Intersection of Law and Medicine
One of Krafft-Ebing’s significant contributions was his work at the intersection of sexual health and legal systems. He testified in cases involving sexual crimes, promoting a deeper understanding of psychological conditions that might influence behavior. Moreover, his involvement in these cases bridged the gap between law and medicine, emphasizing the importance of psychological insights in legal matters.
Influence on Successors
Krafft-Ebing’s pioneering efforts inspired many subsequent sexologists, including Magnus Hirschfeld, Sigmund Freud, and Havelock Ellis. These figures expanded upon his work, exploring themes of sexual identity, gender, and the cultural aspects of human sexuality. In fact, Krafft-Ebing’s influence is evident in the works of these iconic sexologists, who have shaped modern sexology and continue to inform contemporary research and therapy.
REDISCOVERING THE ARCHITECTS OF SEXOLOGY
Commemorating The Visionaries Who Molded Our Perception Of Human Desire
Legacy of Richard von Krafft-Ebing in Modern Sex Therapy
Today, Krafft-Ebing’s influence can be seen in various aspects of sexual health education and therapy. His contributions remain a cornerstone of contemporary sexology.
1. Clinical Framework for Understanding Sexual Disorders
His methodologies continue to inform contemporary approaches to diagnosing and treating sexual dysfunctions and paraphilic disorders. For example, his detailed classifications of sexual behaviors laid the foundation for how clinicians assess and approach sexual health concerns.
2. Normalization of Sexual Conversations
Krafft-Ebing’s decision to document sexual behaviors scientifically helped destigmatize topics that were once considered taboo. Consequently, his work paved the way for open discussions in sex therapy sessions, encouraging more transparent conversations about sexuality.
3. Foundation for Further Research
His detailed case studies remain valuable resources for researchers and clinicians exploring the complexities of human sexuality. As a result, his work continues to inspire new avenues of research and clinical practices, guiding the study of sexual behavior and identity in today’s world.
1. Psychopathia Sexualis: A Groundbreaking Work
In 1886, Krafft-Ebing published Psychopathia Sexualis, a compendium of over 200 case studies documenting a range of sexual behaviors and psychological conditions. This text, primarily written for medical professionals, marked a turning point in vintage sexology. It laid the foundation for the scientific study of human sexuality and established Krafft-Ebing as a key figure in the field.
Key Features of Psychopathia Sexualis
1. Introduction of Terminology
Krafft-Ebing coined terms like “sadism” and “masochism,” inspired by literary figures such as Marquis de Sade and Leopold von Sacher-Masoch. These terms remain central to modern discussions in sex therapy and psychology. By introducing these terms, Krafft-Ebing helped to bring previously stigmatized behaviors into the scientific realm, enabling a more objective exploration of human sexuality.
2. Scientific Rigor
In contrast to prevailing moralistic views, Krafft-Ebing’s work applied a methodical, scientific lens to human sexuality. He argued that many sexual “deviations” were not moral failings, but rather the result of biological, psychological, or social factors. Therefore, his approach paved the way for a more compassionate, evidence-based understanding of sexual behaviors. This was a significant shift from the moralistic perspectives that had dominated before.
3. Influence on Mental Health Practices
By linking sexual behavior with mental health, Krafft-Ebing emphasized the need to address sexual concerns within a therapeutic framework. His work laid the groundwork for what is now a central practice in sex therapy: integrating sexual health into the broader scope of mental health treatment. As a result, the connection between sexuality and psychological well-being became a critical focus in modern therapeutic practices.
Criticisms and Modern Perspectives
While Krafft-Ebing’s contributions to sexology were groundbreaking, they were not without their limitations. Critics, for instance, argue that his focus on categorization sometimes pathologized behaviors that are now recognized as natural variations of human sexuality. For example, his portrayal of homosexuality as a “pathological condition” reflected the biases of his era rather than objective science.
Despite these shortcomings, Krafft-Ebing’s emphasis on empirical research over moral judgment set the stage for modern sex therapy and the broader field of sexology. His work serves as a reminder of the importance of continual reevaluation and adaptation in scientific inquiry.
Fun Facts and Lesser-Known Details About Richard von Krafft-Ebing
Interest in Literature: In addition to his scientific work, Krafft-Ebing was an avid reader of classical literature and often drew from literary themes to explain psychological concepts. His coining of “sadism” and “masochism” was directly inspired by literature.
Pioneer of Patient Rights: Moreover, at a time when psychiatric patients were often stigmatized, Krafft-Ebing advocated for humane treatment and emphasized the importance of understanding the personal narratives of his patients.
Hobbyist Botanist: Furthermore, Krafft-Ebing had a passion for botany and often compared the diversity of plants to the variety in human sexuality, reflecting his appreciation for nature’s complexity.

Richard von Krafft-Ebing (Bildausschnitt), D. Lippay, 1896, Öl auf Leinwand © GrazMuseum
Conclusion
Richard von Krafft-Ebing was more than a psychiatrist; he was a trailblazer who challenged societal norms and expanded the boundaries of scientific inquiry. As a result, his contributions to vintage sexology and modern sex therapy have left an indelible mark on our understanding of human sexuality.
In conclusion, as we continue to explore the complexities of sexual behavior and identity, Krafft-Ebing’s legacy reminds us of the importance of empathy, open-mindedness, and scientific rigor in the pursuit of knowledge.